Cyto Conference 2024
Edinburgh International Convention Center 150 Morrison St, Edinburgh, United KingdomJoin Discovery Life Sciences at Cyto Conference 2024 May 4-8, 2024 | Edinburgh International Convention Center, Edinburgh, Scotland
Predict neutropenia, severe anemia, or thrombocytopenia at the preclinical drug development stage.
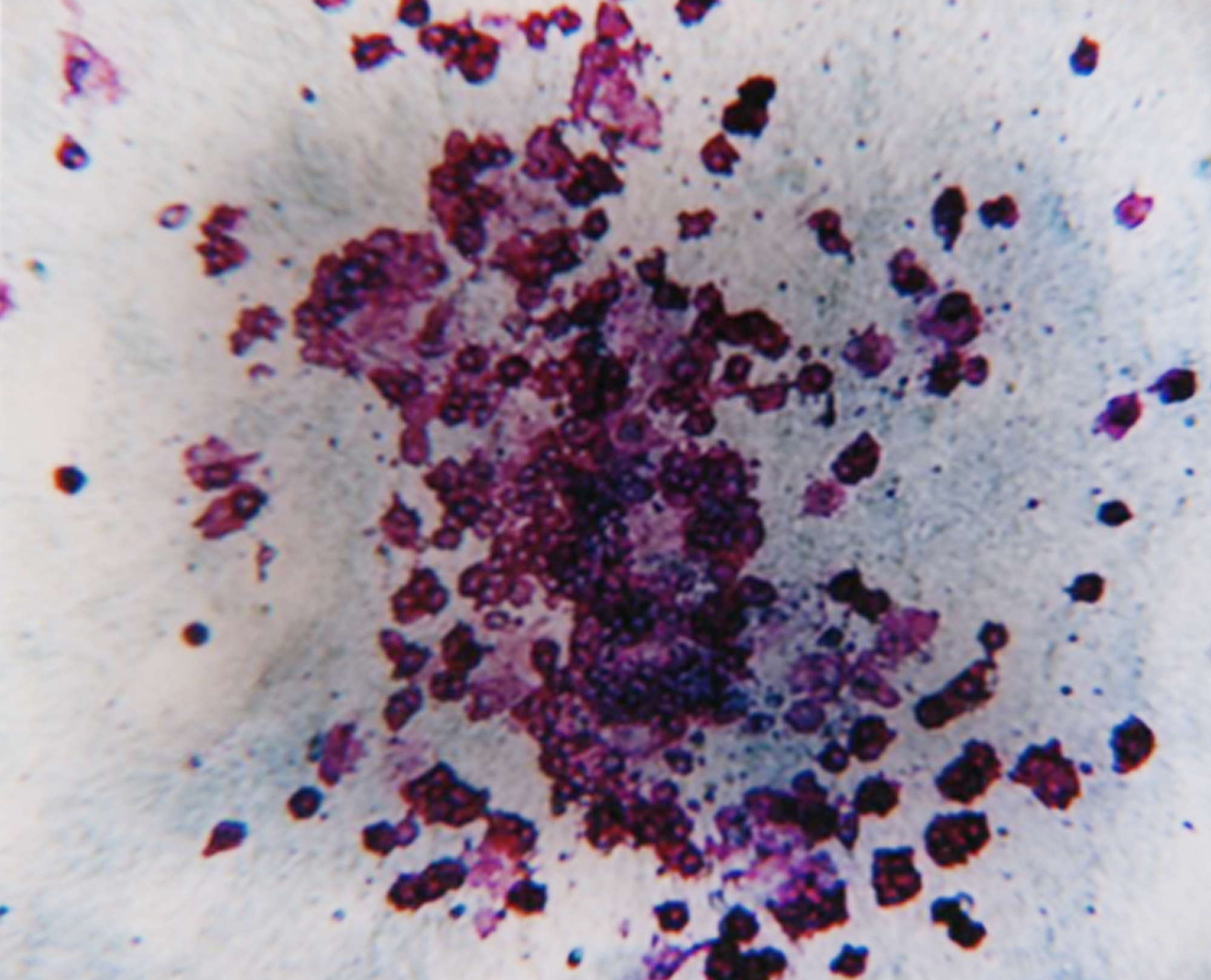
We have decades of experience performing these assays, so you can trust our cell culture proficiency and lineage-specific colony scoring accuracy. CFC assay data can support your IND submission and these assays are often required by regulatory agencies. CFC assays are highly effective in predicting toxicity at the bone marrow hematopoietic progenitor cell level and can be utilized to evaluate drug efficacy against blood cancer progenitor cells.
The preclinical screening method that helps clients eliminate bad players earlier in the drug development process. White Paper
Colony Forming Cell assays can predict compound induced toxicities including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia and lymphotoxicity. Video
The haematotoxic potential of xenobiotics is determined by the evaluation of the inhibition of CFU-GM growth. White Paper

Join Discovery Life Sciences at Cyto Conference 2024 May 4-8, 2024 | Edinburgh International Convention Center, Edinburgh, Scotland
Join Discovery Life Sciences at APT 2024 May 14-16, 2024 | Merck Research Laboratories, Boston, Massachusetts
Join Discovery Life Sciences at ISCT 2024 Stop by our booth #453 or schedule a meeting with our CGT team. May 28- 31, 2024 | Vancouver, Canada
Copyright © 2024 Discovery Life Sciences. All rights reserved.
Designed & Developed by Altitude Marketing