I/O Summit Europe 2024
Hilton London Canary Wharf S Quay Square, Marsh Wall, London, United KingdomJoin Discovery Life Sciences at I/O Summit Europe 2024 April 23-25, 2024 | Hilton London Canary Wharf, London, England
Evaluate drug efficacy or toxicity rapidly and reliably using highly customizable blood cell-based assays.

Discovery’s preclinical experts have decades of experience in hematopoietic cell development and evaluation. We can assess your drug candidates in fit-for-purpose assays to study drug efficacy or deleterious drug effects.
Our in vitro blood cell-based assays account for nuanced cell culture requirements to ensure that you receive biologically relevant data. We also welcome the opportunity to develop and execute customized studies, or to replicate published assays using your therapeutic candidates.
Discovery’s HbF induction assay service screens drugs for their ability to increase levels of fetal hemoglobin (HbF), a high affinity oxygen transport protein that has been successful in easing serious hemoglobinopathy impacts.
Our service offers the ability to screen multiple compounds at once and allows for HbF induction comparison between test drugs and hydroxyurea (HU), the current, but suboptimal, standard of care for sickle cell disease (SCD) treatment.
Advanced, IND-Enabling Drug Screening for SCD and Hemoglobinopathies
Discovery’s antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) assay services help assess yourantibody's ability to facilitate effector cell-mediated cell killing by natural killer (NK) cells. Our experts can also help you screen your antibodies for complement events in our complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) assay.
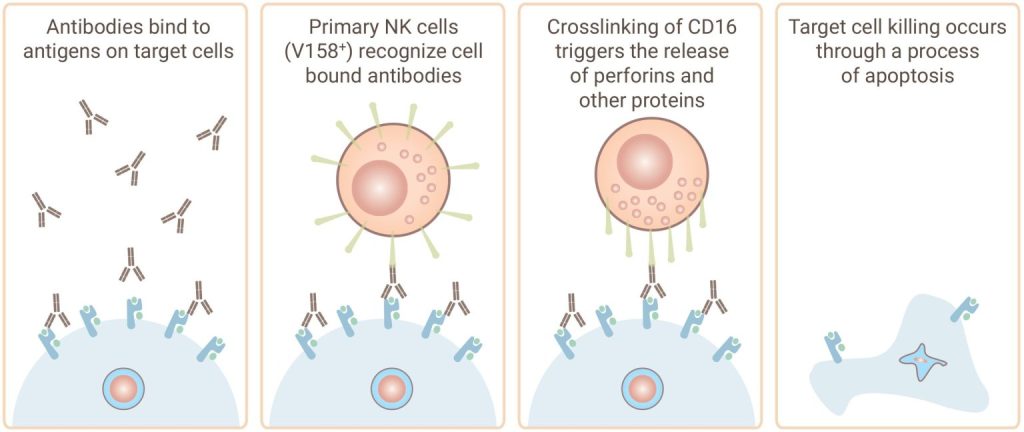
Gentest® ADCC Assay Service
Gentest® CDC Assay Services
By utilizing our state-of-the-art technologies and expert knowledge, Discovery’s mast cell activation (MCA) assay service helps preclinical researchers identify compounds that could potentially reverse mast cell activation, as measured by CD63 expression.
While megakaryocytic colony forming cell (CFC) assays are predictive of thrombocytopenia caused by drugs impacting the primitive progenitor stage, toxicity can also occur at later stages of cell development.
Discovery’s megakaryocyte maturation and platelet development assay services assess the off-target toxicity potential of your drug candidate on developing megakaryocytes and megakaryocyte-derived platelets at different stages of cell development.
While myeloid and erythroid colony forming cell (CFC) assays are predictive of neutropenia and severe anemia caused by drugs impacting the primitive progenitor stage, toxicity can also occur at later stages of cell development.
Discovery’s myeloid and erythroid cell maturation assay services further assess the off-target toxicity potential of your drug candidate on developing neutrophils and red blood cells at different stages of cell development.
Discovery has a team of highly skilled and collaborative cell biology experts who can replicate protocols or publications you would like to use for evaluating the function of your compounds.
Additionally, you have the option to choose from one of Discovery’s standard assay platforms. Experienced in replicating blood cell-based protocols and publications.

Join Discovery Life Sciences at I/O Summit Europe 2024 April 23-25, 2024 | Hilton London Canary Wharf, London, England
Join Discovery Life Sciences in Booth #11 at CB & CDx London 2024 April 24-25, 2024 | Millennium Gloucester Hotel London Kensington, London, England
Join Discovery Life Sciences at Cyto Conference 2024 May 4-8, 2024 | Edinburgh International Convention Center, Edinburgh, Scotland
Copyright © 2024 Discovery Life Sciences. All rights reserved.
Designed & Developed by Altitude Marketing