I/O Summit Europe 2024
Hilton London Canary Wharf S Quay Square, Marsh Wall, London, United KingdomJoin Discovery Life Sciences at I/O Summit Europe 2024 April 23-25, 2024 | Hilton London Canary Wharf, London, England
Predict thrombocytopenia at the preclinical drug development stage.

These in vitro assays replicate in vivo cell biology conditions. We incubate primary bone marrow cells with your test compounds in a collagen-based matrix containing specific growth factors. We then fix and stain the cultures for CD41, count the colonies, and provide you with a detailed report on your drug’s off-target toxicity impact.
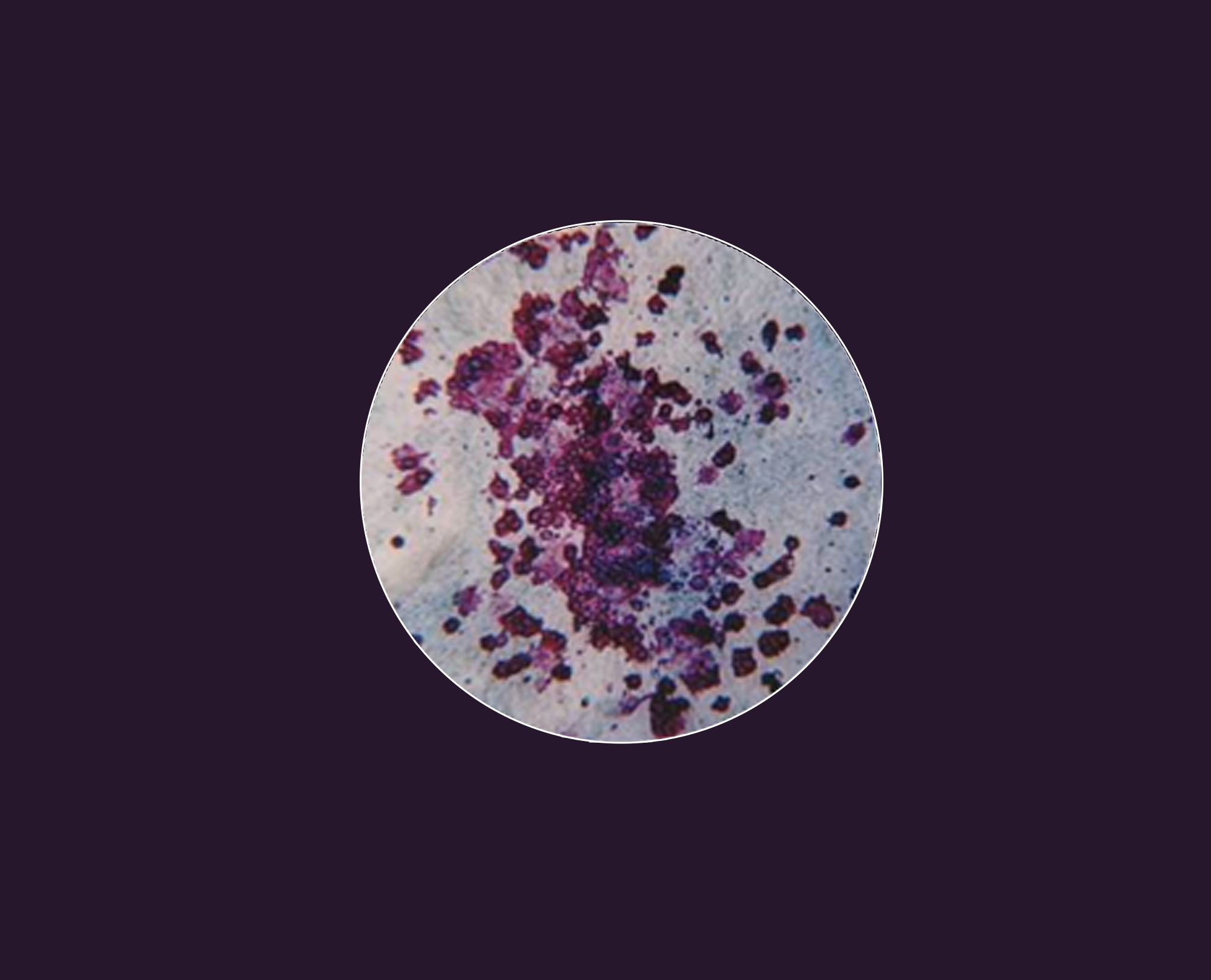
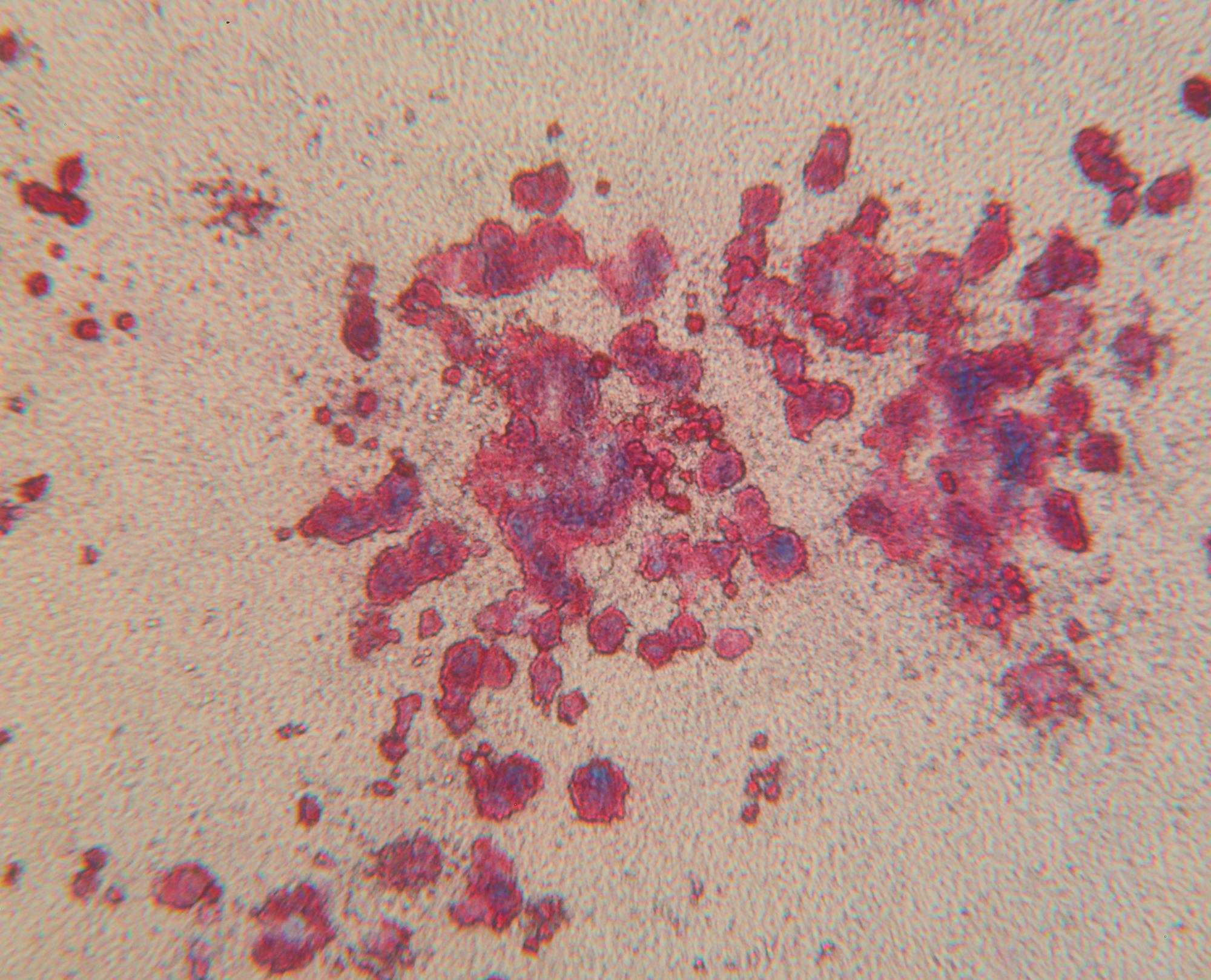
The preclinical screening method that helps clients eliminate bad players earlier in the drug development process. Whitepaper
A quick reference resource for scientists who need to isolate, manipulate, or develop assays involving human mononuclear cells. Video
This in vitro assay has been validated by ECVAM (European Centre for the Validation of Alternative Methods) and correlates well with clinical neutropenia for many drug classes. Protocol

Join Discovery Life Sciences at I/O Summit Europe 2024 April 23-25, 2024 | Hilton London Canary Wharf, London, England
Join Discovery Life Sciences in Booth #11 at CB & CDx London 2024 April 24-25, 2024 | Millennium Gloucester Hotel London Kensington, London, England
Join Discovery Life Sciences at Cyto Conference 2024 May 4-8, 2024 | Edinburgh International Convention Center, Edinburgh, Scotland
Copyright © 2024 Discovery Life Sciences. All rights reserved.
Designed & Developed by Altitude Marketing